Printing a small model perfectly with a 3D printer requires a lot of training to perfect the art. And as you might have seen, 3D printers print models of all shapes and sizes.
But how small can a 3D printer print?
Today’s article delves into miniature 3D printing, factors to consider when printing small 3D prints, and limitations you may encounter.
Read on.
How Small Can 3D Printers Print?
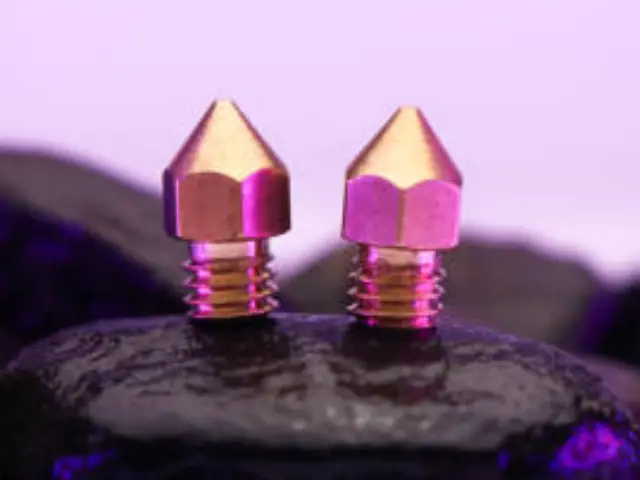

Smaller nozzles can print smaller models than nozzles with greater diameters. Additionally, the nozzle’s diameter determines the printer’s additive manufacturing process.
Some 3D printers can print micron-sized and nanometer-sized projects.
Types of 3D Printers and How Small They Can Print
The most common types of 3D printers are:
Fused Deposition Modeling 3D Printers
FDM printers feature a thermoplastic filament to create a 3D project. The filament is heated to reach its melting point and then extruded through the heated nozzle layer by layer.
These printers are less complicated and create designs faster, thus saving time. Unfortunately, FDM models are susceptible to thermal stresses and may have design inconsistencies.
Nevertheless, FDM printers can print small designs of up to 0.4mm to 0.15mm with a nozzle upgrade. When working on such projects, you need to maintain accuracy since it is impossible to control or stop the flow of the filament.
Stereolithography 3D Printers

SLA printers create 3D models and prototypes with high print accuracy and surface quality. Unlike FDM models, these printers use a laser beam to trace a layer. By doing so, these 3D printers produce detailed plastic designs with smooth finishes.
SLA printers use photopolymerization, a process where liquid resin is compressed in layers to form clear, solid designs. The parts are then fully solidified through a UV-curing cycle for accurate and fine details.
Nevertheless, pay attention to the size of the laser beam spot as it determines the size of your objects.
Digital Light Processing 3D Printers
This 3D printer produces photopolymer parts using a projected light source and liquid resin. DLP 3D printers have a digital light projector that features thousands of micromirrors to reflect light when printing a solid model.
But how small can DLP 3D printers print?
However, you need to be experienced to pull this off.
Here is a YouTube video that explains the differences between the three types of 3D printers.
What Factors Should You Consider When Printing Small 3D Models?
Unlike working with larger models, printing small 3D models can be challenging, especially if you are not sure about the printer’s settings and capabilities. Regardless, here are factors you need to consider when printing miniature 3D models.
Have a Realistic CAD Model
You need to have a precise CAD drawing that fits well with your printer nozzle to print the small 3D model. You can’t have parts missing as it creates voids in your finished product.
And, since the 3D model is small, having missing parts lowers its structural integrity. Additionally, you cannot decide to print the part and fix it in your model if the object is too small.
Support Fragile Objects
Small objects have thin walls that make printing them a complex process. Your model has a high chance of falling apart if you don’t support these delicate parts.
Ensure to add solid support that will not crumble under its weight and that of the model you’re printing. You can permanently remove the support once your model has settled well.
Follow Printing Material Guidelines

3D printers vary depending on their technology and properties. Before printing, be aware of your model’s minimum wall thickness, detail, and clearance. It will ascertain that the model retains a high level of accuracy and strength.
Also, look out for the maximum and minimum size your 3D printer can print. The model’s size depends on the technology you’re using and the nozzle size.
Jump In: In order for your printer to work efficiently and last you a long time, you have to maintain it on a regular basis. Read my blog How To Clean A 3D Printer Nozzle to guide you properly.
How Long Does It Take To 3D Print Small Objects?
The material type, printer quality and type, item complexity, nozzle size, and layer structure determine the time you’ll take for 3D printing small objects.
Generally, printing an object through additive manufacturing depends on the infill and quality settings. Therefore, printing a low-quality setting small object can take 10 to 30 minutes. It will take several hours to print high-quality, complex, and high infill objects.
LCD 3D printing is faster than SLA and FDM 3D printing.

And, I am not saying that the LCD printer will always print faster than the other two. Other factors such as the quality and detail you want to be printed contribute to a 3D printer’s speed. You might have to forego speed if you want a high-quality model.
Additionally, your model’s thickness also determines the time you will take to print. The thicker the model, the more time you will need to print it successfully.
Jump In: Printers do expend energy. The bigger the printing task, the more power it requires. Sometimes, a printer might break down or stop momentarily if overused already. Learn how to properly monitor your printer usage by reading my article, How Much Electric Power Does a 3D Printer Use? for a more detailed explanation.
How Thin Can a 3D Printer Print?
How thin a 3D printer print determines the size of your model. Therefore, the thickness of a small 3D-printed model depends on the size of the printer’s nozzle. Smaller nozzles take more sweeps to print thicker walls and hence can print very thin walls with one sweep.
Your model’s wall thickness, or the least thickness it can have, is an essential parameter in 3D printing. Extremely thin models are complicated to work with since the small diameter nozzles tend to clog relatively easily and require more skill to print.
If you are not experienced in high-detail 3D printing, avoid thinner models as they are more delicate. Additionally, models with a thickness below 2 mm require extra care while transporting.
For example, a model with a thickness that is less than 1 mm might crumble or have its hanging or extended parts breaking off and falling when you design them to be thin.
Here’s the Best Minimum Wall Thickness for Your 3D Models
I should add that some materials are more robust than others and can make thinner models. One such material is high-detail stainless steel.
It has excellent strength, a great resolution, and can produce fine-detail models.
You will print the thinnest models if you opt for stereolithography (SLA), followed by selective laser sintering (SLS), and lastly, fused deposition modeling (FDM).
And if you are new to any of these processes, here are some minimum wall thickness settings you can use.
Stereolithography (SLA)
Use a minimum wall thickness of 0.2 mm for both the supported and unsupported wall models.
You can use a setting of 0.15 mm for minimum recession engraved detail models and 0.1 mm for minimum protrusion embossed detail models.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
Use a minimum wall thickness of 0.7 mm for supported and 1 mm for unsupported wall models.
Also, use a setting of 0.2 mm wide for minimum recession engraved detail models and 0.2 mm wide for minimum protrusion embossed detail models.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
Use a minimum wall thickness of 1 mm for supported and unsupported wall models.
Use a 2 mm deep and 0.6 mm wide setting for the minimum recession engraved detail, and minimum protrusion embossed detail models.
What Are the Limitations of Thin-Wall 3D Printing?
3D printing of thin models requires extra precaution and a clear understanding of your object’s size. For bigger objects, set your 3D printer to print thicker walls.

However, knowing the exact thickness can be challenging for newbies. You would not want to print an object that is too thick as it will be more expensive and consume more time than necessary. Additionally, you need to understand that printing larger models may require a good understanding of thin wall printing.
Another challenge with thin wall printing is breaking during the post-print processes of cleaning the model.
Thin models need support structures while printing out.
Once you remove the support during the post-print cleaning process, your model is more likely to break if it cannot handle its weight.
Related Questions
Can you 3D print 1mm?
Yes. You can print 1mm models because your printer’s nozzle is 1mm thick or less.
Can you 3D print small metallic models?
Yes, we have metal additive manufacturing processes that allow you to print small 3D items. Steel, titanium, stainless steel, copper, cobalt, aluminum, tungsten, chrome, and titanium are common metals used in 3D printing.
Conclusion
3D printers can only print objects as small as the diameter of their nozzles. Therefore, purchase smaller third-party nozzles if you want to print tiny objects.
Printing small models can be fun if you know how to do it well. Take time to study the art, and you will be printing your small models in no time.
Last Updated on July 21, 2022 by Emily
- Facebook9
- Twitter21
- Pinterest67
- 97shares




